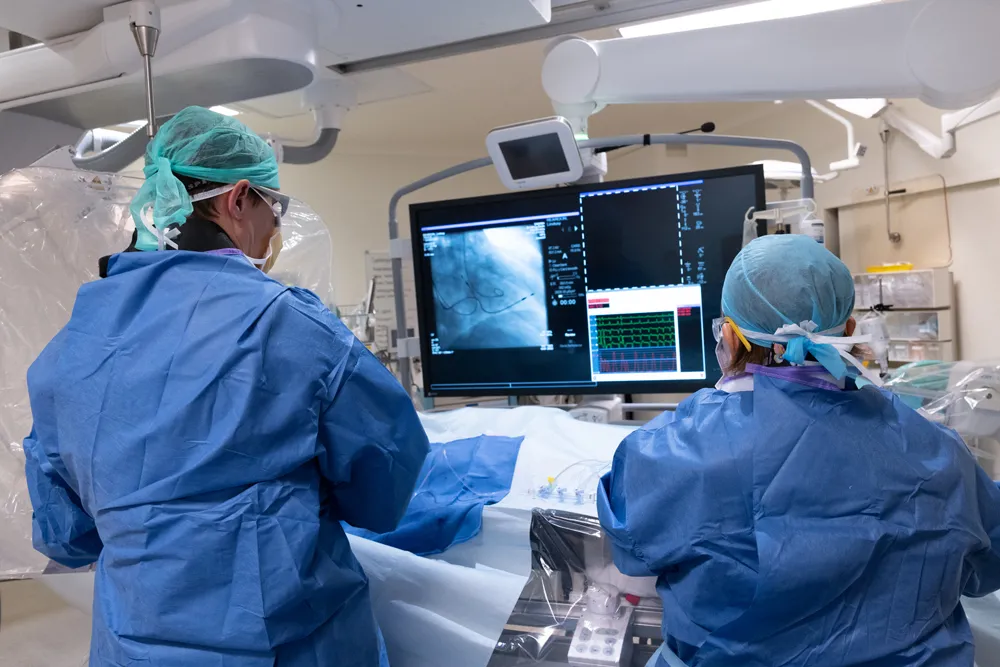
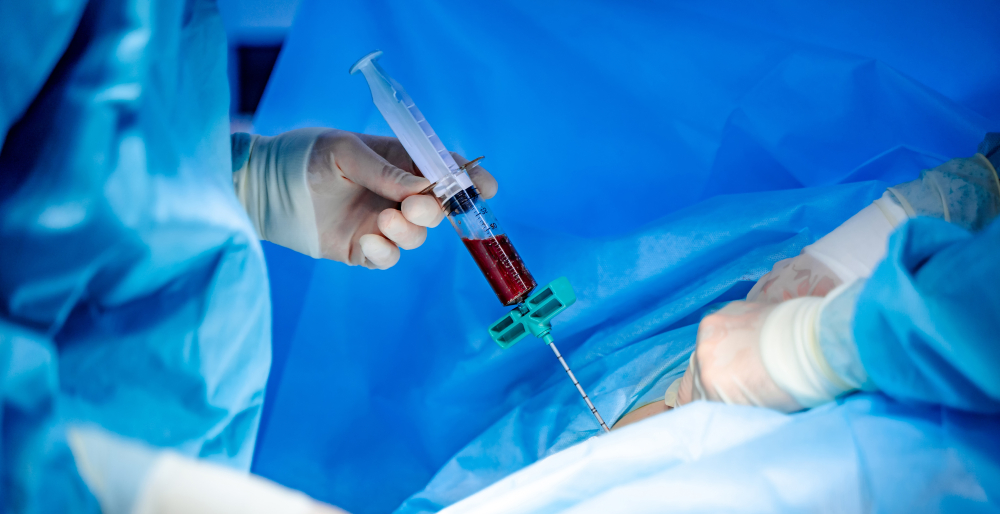
Angioplasty & Stenting
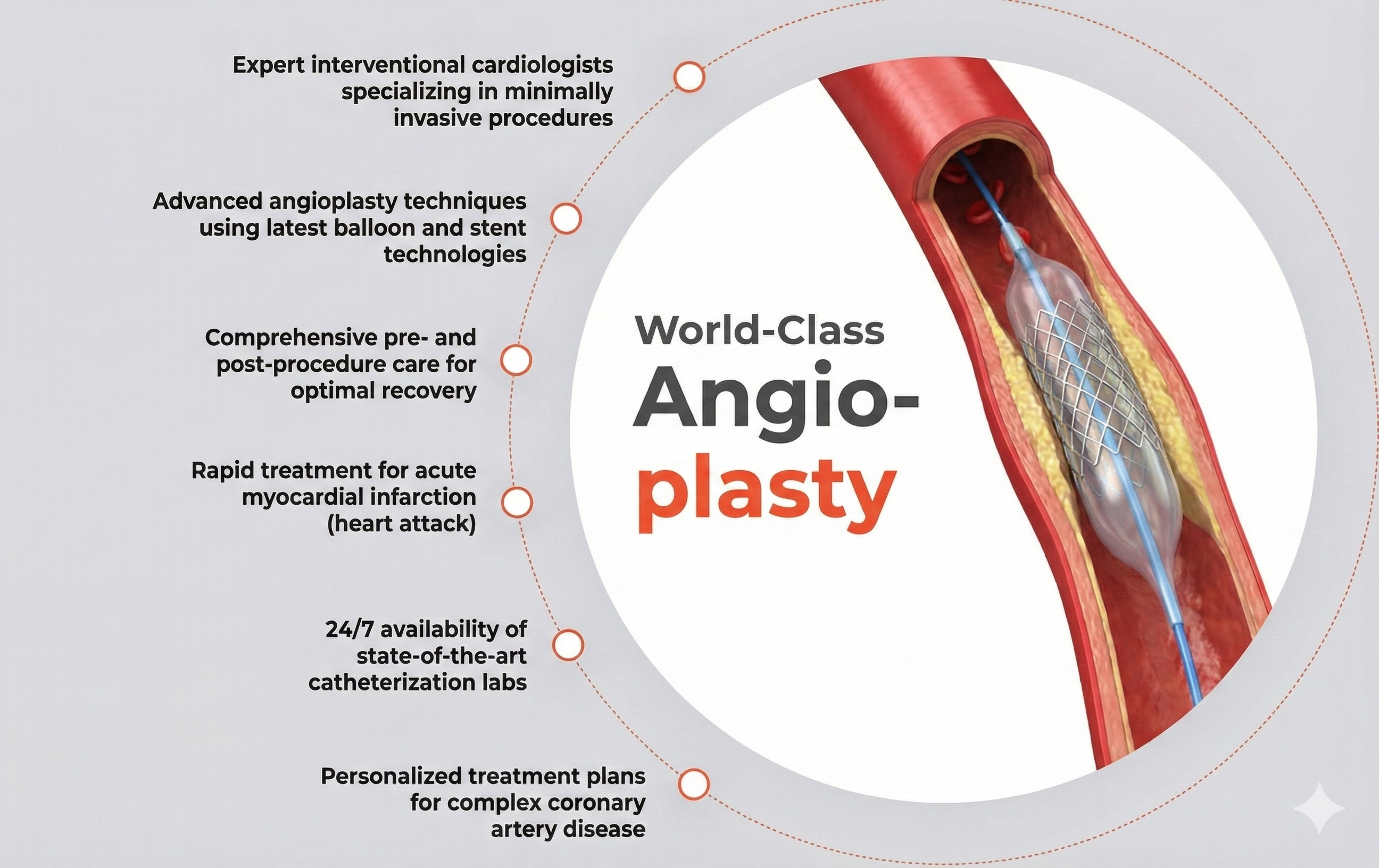

Angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, typically arteries, to restore normal blood flow. Often performed to treat coronary artery disease...
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, typically arteries, to restore normal blood flow. Often performed to treat coronary artery disease, it involves threading a thin catheter with a small balloon at its tip to the affected area. Once in place, the balloon is inflated to compress plaque against the artery walls, widening the vessel. In many cases, a stent—a small mesh tube—is inserted to keep the artery open long-term. Angioplasty helps relieve symptoms like chest pain, improves heart function, and can reduce the risk of heart attack.
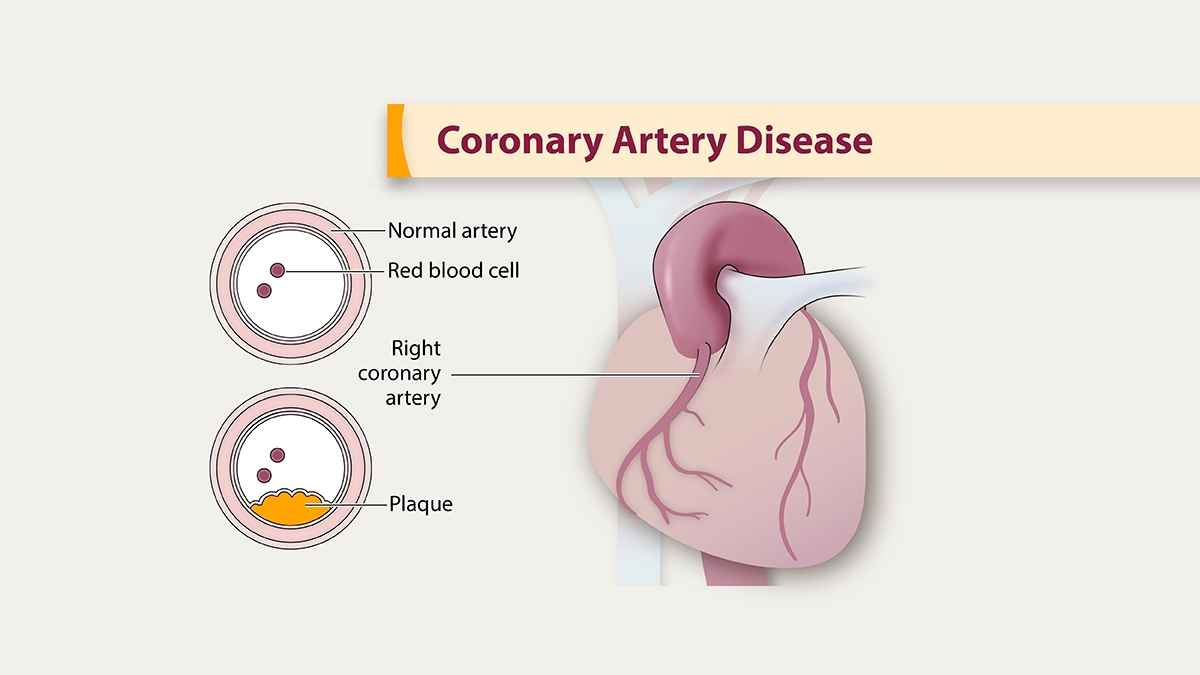
CAD occurs when the coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This can cause chest pain (angina) or increase the risk of a heart attack.
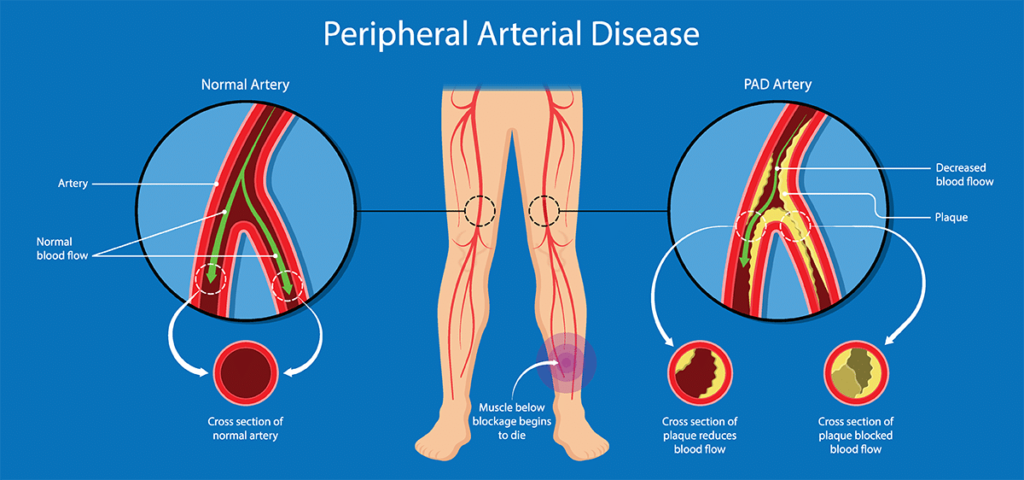
PAD is the narrowing or blockage of arteries in the limbs, usually the legs, leading to pain, cramping, or poor circulation.
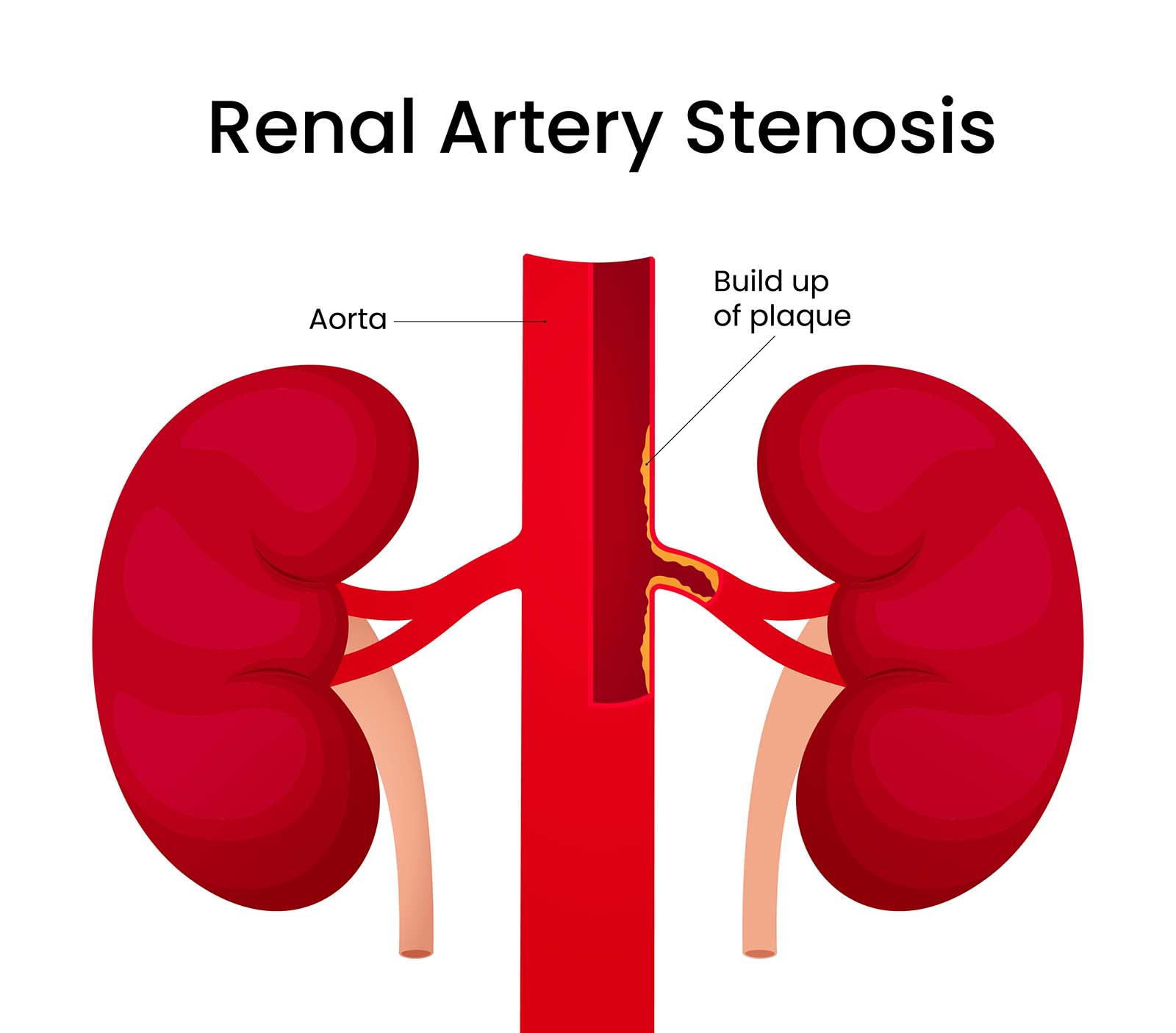
This condition involves narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys, which can lead to high blood pressure and kidney damage.
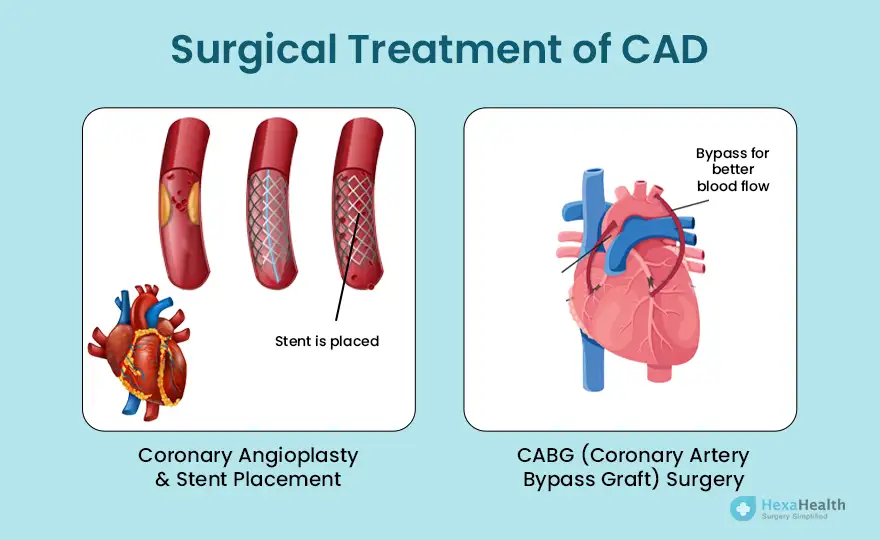
A balloon-tipped catheter is used to widen the blocked artery, often followed by placing a stent to keep it open and restore proper blood flow.
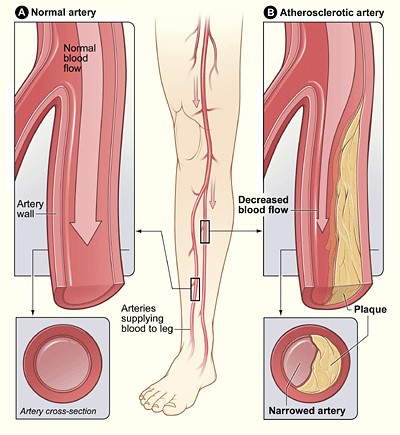
Angioplasty widens the affected arteries, sometimes with stent placement, improving blood flow and relieving symptoms.
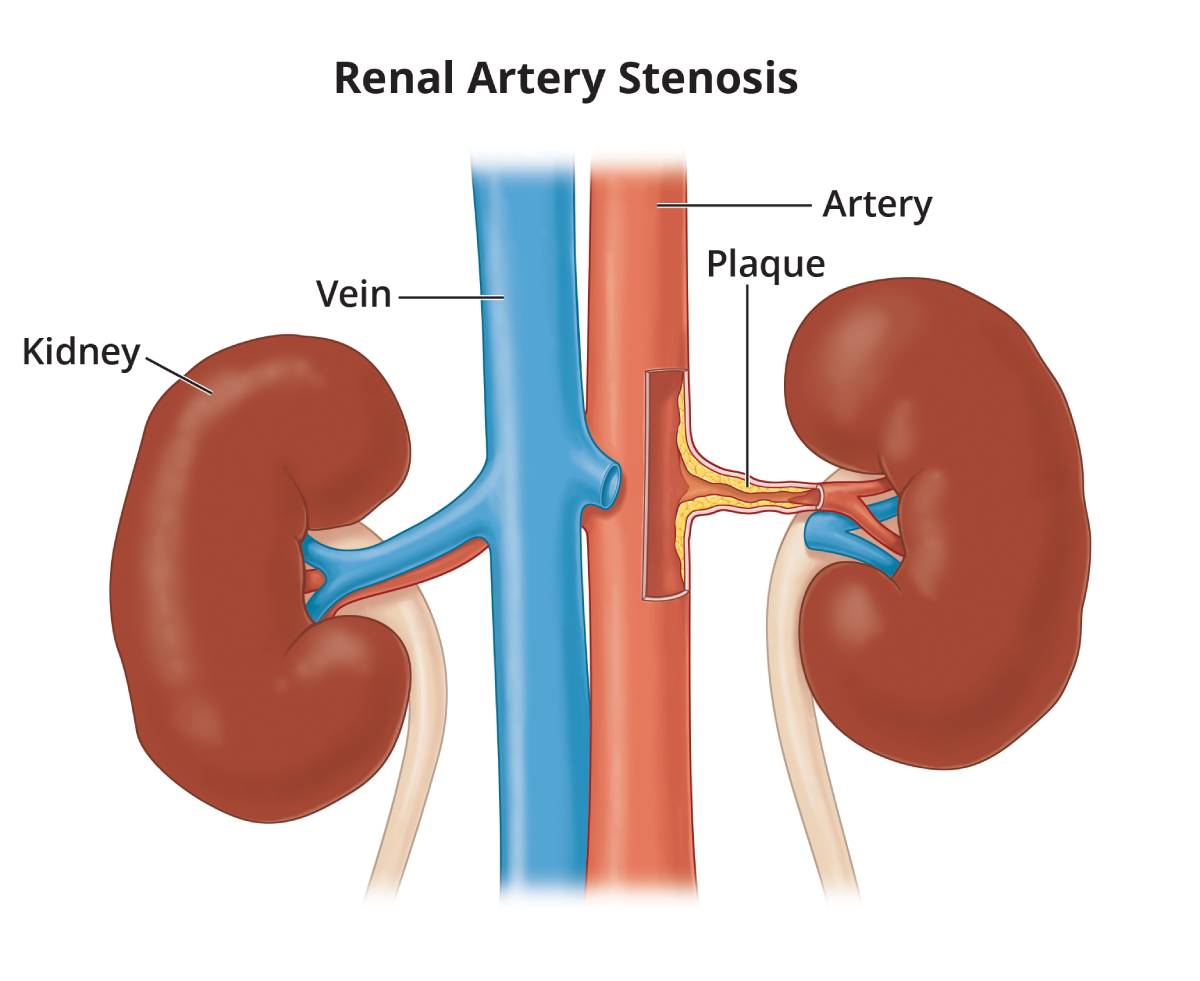
Balloon angioplasty, often with stenting, opens the narrowed renal artery, restoring adequate blood flow and helping control blood pressure.
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, typically arteries, to restore normal blood flow. Often performed to treat coronary artery disease, it involves threading a thin catheter with a small balloon at its tip to the affected area. Once i
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, typically arteries, to restore normal blood flow. Often performed to treat coronary artery disease, it involves threading a thin catheter with a small balloon at its tip to the affected area. Once in place, the balloon is inflated to compress plaque against the artery walls, widening the vessel. In many cases, a stent—a small mesh tube—is inserted to keep the artery open long-term. Angioplasty helps relieve symptoms like chest pain, improves heart function, and can reduce the risk of heart attack.